
Coordinator: Matteo Cadeddu
Research INFN – Cagliari Unit
@ Physics Department
Room: 1AA8
Phone: + 39 070/675 4982
E-mail:matteo.cadeddu@ca.infn.it
The activities related to astroparticles and fundamental physics are coordinated on a national basis by the Scientific Commission 2 of the National Institute of Nuclear Physics. The Cagliari Unit contributes to several projects both in the field of cosmic ray physics and in the field of gravitational wave physics.
Einstein Telescope (ET)
The Einstein Telescope (ET) is a scientific project for the construction of a new gravitational wave observatory. The ET detector will be a system of interferometers with an improved sensitivity compared to current detectors such as LIGO/Virgo. In particular, its excellent detection capabilities for low frequency signals coming from cosmological events in the early universe will open a new window on our understanding of the cosmos.
The region around the Sos Enathos mine, in Sardinia, is one of the main candidates as hosting site for the observatory due to extremely low seismic and anthropic noise figures. The final choice of the site will happen by 2025.
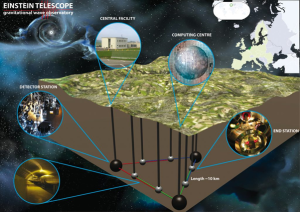
The ET international collaboration, officially established in 2022, counts more than 1400 scientists around the globe. The INFN ET group in Cagliari strongly contributes to the Sos Enathos site characterisation and theoretical studies on the expected Newtonian noise level. The Cagliari ET Research Unit, lead by INFN, also includes members from the University of Cagliari, CNR, OAC, CREF, CINIgeo, INAF-OAC for a total of about 50 persons. Their expertise on various scientific and technical aspects of this endeavour will play a crucial role in construction and management of the observatory.
Contacts:
- Research Unit Leader: Andrea Contu (andrea.contu@ca.infn.it)
- Outreach&Education ResponsibleMatteo Tuveri (matteo.tuveri@ca.infn.it)
DARKSIDE
The Darkside experiment has as its objective the research of WIMP Dark Matter (Weakly Interacting Massive Particle) through its interaction with the argon atoms in liquid phase. The experiment located at the National Laboratory of the Gran Sasso of INFN, consists of three phases: DarkSide-50 (DS50), a 50 Kg double-phase temporal projection chamber and two-year data acquisition, DarkSide-proto 1t , under construction and testing at CERN in Geneva, and DarkSide-20k, in an advanced design phase, from 20t, which will take data from 2021. Recently, DS50 has published the best limit in the world for the research of WIMP Dark matter with low masses.
 A fundamental element of DS20k, on which a part of the group is actively engaged, is the cryogenic distillation column Aria, during assembly at the Carbosulcis mine in Nuraxi-Figus (CI), which will allow both to purify the argon for impurity DS20k and, for DarkSide-Proto, to reduce the content of the radioactive isotope of mass number 39 by a factor of about 10 per passage.
A fundamental element of DS20k, on which a part of the group is actively engaged, is the cryogenic distillation column Aria, during assembly at the Carbosulcis mine in Nuraxi-Figus (CI), which will allow both to purify the argon for impurity DS20k and, for DarkSide-Proto, to reduce the content of the radioactive isotope of mass number 39 by a factor of about 10 per passage.
The Cagliari unit also conducts research in the following areas: theory and phenomenology of WIMP interaction, data analysis of DS50, development of an optical transmitter for analog signals in liquid argon and design of the DArT detector for measurement of the radioactivity of argon, which is thought to be installed at the Canfranc laboratory in Spain. It also participates in measurements on the ReD detector, a double-phase chamber of a few Kg, at the University of Naples, for calibration purposes and for the possible measurement of directional effects of the interaction of the WIMPs in the detector.
The Group’s Researchers have various coordination tasks within both DS20k (Project Scientist) and Aria (Relations with Local Authorities and Deputy-Technical Coordinators)

In the photo, the assembly of the Seruci-0 test column of the Cryogenic distillation plant Aria at CarboSulcis (CI).
The activities related to astroparticles and fundamental physics are coordinated on a national basis by the Scientific Commission 2 of the National Institute of Nuclear Physics. The Cagliari Unit contributes to several projects both in the field of cosmic ray physics and in the field of gravitational wave physics.
